産総研/山添主任研究員らの研究成果がACS Applied Materials & Interfacesに掲載されました
多数の機能を備えたマイクロマシンの開発
- 異なる機能を持つパーツを組み合わせて高機能なマイクロマシンを作る -
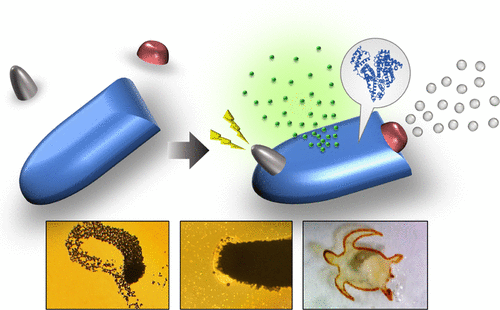
国立研究開発法人 産業技術総合研究所 バイオメディカル研究部門 細胞・生体医工学研究グループ 山添 泰宗主任研究員は、インクジェットプリンターを利用して特定のタンパク質でできたマイクロメートルサイズのパーツ(パーツは構成タンパク質の機能を持つ)を合体させることで、多数の機能を備えた高度なマイクロマシンを作ることに成功しました。
Abstract
Untethered mobile micromachines have considerable potential to realize more effective and minimally invasive medicine. Although diverse medical micromachines have been reported over the past few decades, these machines were developed for performing only specific tasks and the functions imparted to them were limited to a few. Hence, the methodologies for imparting a wide variety of functions to machines have not been fully explored. In this study, a novel construction strategy for the multifunctional micromachines is presented, where a specific function can be added to the machine in one step by directly combining the protein-based component, possessing the biological function of constituent proteins, to an arbitrary position of the machine by using an inkjet printing technique. As a proof-of-concept demonstration, various types of machines were constructed by combining multiple components with different functions. These constructed machines successfully performed functions as diverse as enzyme-powered self-propulsion, collection of target objects, including the bilirubin and living cells, enzyme-mediated conversion of substrate molecules to different ones, magnetic guidance, and release of anti-inflammatory drug diapocynin. The study’s progressive approach as well as multifunctional and biocompatible machines composed of proteins will profoundly impact the development of intelligent machines equipped with multiplex sophisticated functionalities.
Untethered mobile micromachines have considerable potential to realize more effective and minimally invasive medicine. Although diverse medical micromachines have been reported over the past few decades, these machines were developed for performing only specific tasks and the functions imparted to them were limited to a few. Hence, the methodologies for imparting a wide variety of functions to machines have not been fully explored. In this study, a novel construction strategy for the multifunctional micromachines is presented, where a specific function can be added to the machine in one step by directly combining the protein-based component, possessing the biological function of constituent proteins, to an arbitrary position of the machine by using an inkjet printing technique. As a proof-of-concept demonstration, various types of machines were constructed by combining multiple components with different functions. These constructed machines successfully performed functions as diverse as enzyme-powered self-propulsion, collection of target objects, including the bilirubin and living cells, enzyme-mediated conversion of substrate molecules to different ones, magnetic guidance, and release of anti-inflammatory drug diapocynin. The study’s progressive approach as well as multifunctional and biocompatible machines composed of proteins will profoundly impact the development of intelligent machines equipped with multiplex sophisticated functionalities.
掲載論文のご案内
この研究成果は、ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces誌に掲載されています。
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces掲載論文
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces誌 論文ページ
論文情報
| タイトル | Multifunctional Micromachines Constructed by Combining Multiple Protein-Based Components with Different Functions |
|---|---|
| 掲載誌 | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces |
| 著者 | Hironori Yamazoe National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), 1-8-31 Midorigaoka, Ikeda, Osaka 563-8577, Japan |
| 掲載⽇ | 2023年12月11日 |
| DOI | 10.1021/acsami.3c12912 |
